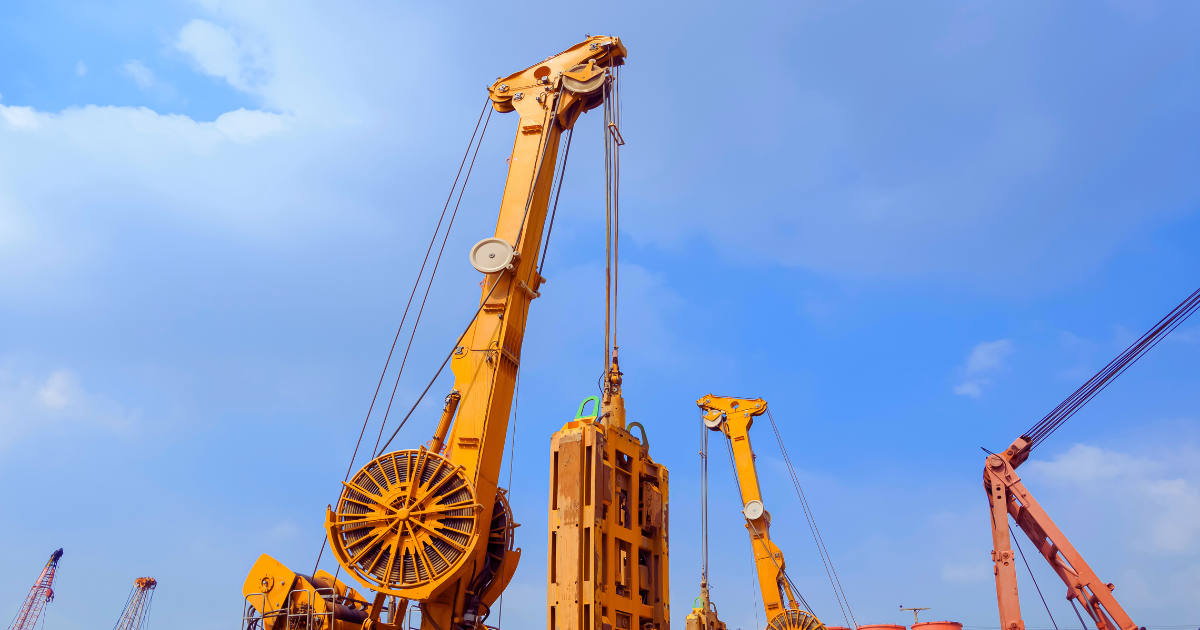
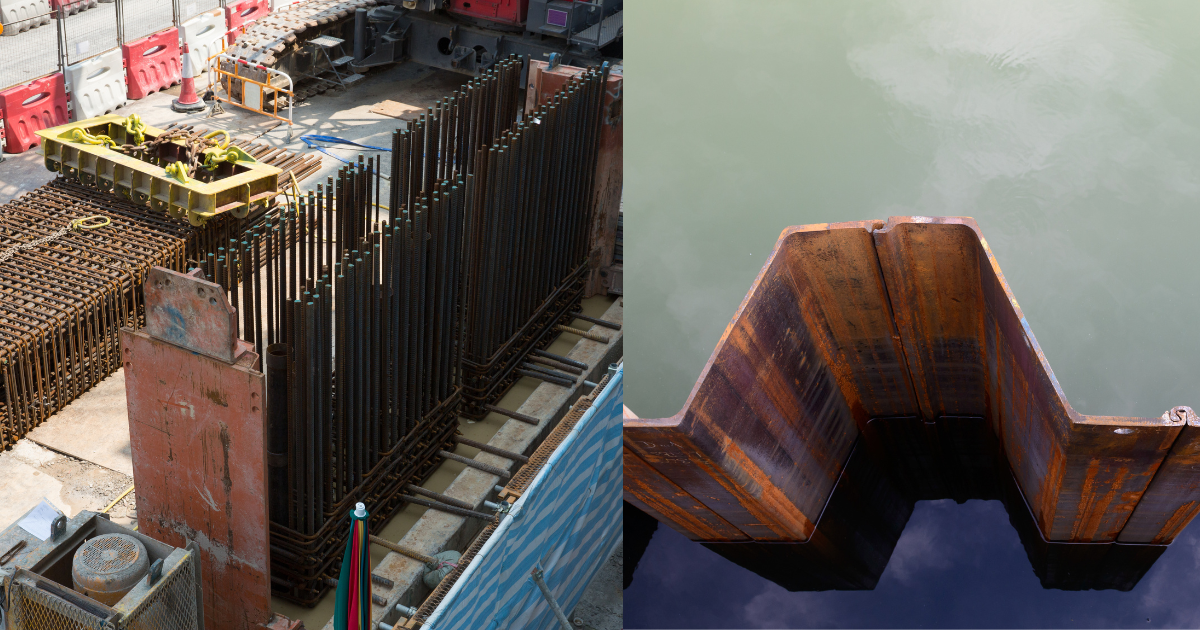
Retaining structures are essential for various construction projects, especially those involving deep excavations, foundation systems, and soil stabilization. Among the most commonly used techniques are Diaphragm Wall and sheet piling. Each method offers unique benefits and is suited to specific project requirements. Understanding their differences can help engineers and project managers choose the best solution for their construction needs. This blog delves into the comparison of Diaphragm Wall and sheet piling, examining their applications, advantages, challenges, and suitability for different scenarios.
What are Diaphragm Walls?
A Diaphragm Wall is a reinforced concrete structure used primarily as a retaining wall or part of a foundation. These walls are constructed by excavating a trench, reinforcing it with steel cages, and then pouring concrete to create a robust, watertight barrier. Diaphragm Walls are highly effective in projects requiring deep excavation and are often used in high-rise building foundations, underground parking structures, and tunnels.
Advantages of Diaphragm Walls:
- High Strength and Stability: These walls are capable of withstanding significant loads and are suitable for deep excavations.
- Waterproofing: They provide excellent water resistance, making them ideal for projects in high-water table areas.
- Long Lifespan: Their durability ensures minimal maintenance over time.
- Low Noise and Vibration: The construction process generates minimal environmental impact, making it suitable for urban areas.
What is Sheet Piling?
Sheet piling involves driving pre-fabricated steel, vinyl, or composite sheets into the ground to form a continuous wall. These walls are primarily used as temporary or permanent retaining structures in shallow or medium-depth excavations. Sheet piles interlock to create a barrier against soil and water movement.
Advantages of Sheet Piling:
- Quick Installation: Sheet piles are pre-fabricated, which speeds up the construction process.
- Cost-Effective for Shallow Depths: This method is economical for projects that do not require deep excavation.
- Reusability: Steel sheet piles can be removed and reused in other projects.
- Versatility: They can be adapted to various site conditions and soil types.
Comparing Diaphragm Walls and Sheet Piling
1. Application Areas
- Diaphragm Walls:
Best suited for large-scale infrastructure projects like high-rise foundations, metro stations, and dams. They are preferred in scenarios requiring deep excavations and watertight barriers. - Sheet Piling:
Typically used for temporary structures, coastal protection, and shallow excavations. It is more suitable for projects requiring quick and cost-effective solutions.
2. Structural Strength
- Diaphragm Walls:
These walls offer superior structural strength, enabling them to support heavy loads and resist significant lateral earth pressures. - Sheet Piling:
While adequate for shallow depths, sheet piling lacks the strength to handle the pressures encountered in deep excavations.
3. Water Resistance
- Diaphragm Walls:
Provide excellent water-tightness, making them the go-to choice for projects in high-water table areas or where groundwater control is critical. - Sheet Piling:
Although interlocking sheet piles offer some water resistance, they are not as effective as Diaphragm Walls in completely sealing out water.
4. Cost Implications
- Diaphragm Walls:
The construction process is more expensive due to the need for specialized equipment, materials, and skilled labor. However, their durability and long-term performance can offset the initial costs. - Sheet Piling:
A more cost-effective solution for temporary or less demanding applications. The reusability of sheet piles further reduces costs.
5. Environmental Impact
- Diaphragm Walls:
The low noise and vibration during construction make this method environmentally friendly and suitable for urban areas. - Sheet Piling:
Driving sheet piles can produce noise and vibrations, which may not be ideal for densely populated or sensitive areas.
6. Installation Time
- Diaphragm Walls:
Require more time due to the trench excavation, reinforcement, and concrete pouring processes. - Sheet Piling:
Offers faster installation, making it a preferred choice for projects with tight timelines.
When to Choose Diaphragm Walls?
- Deep excavations exceeding 20 meters.
- Projects in high-water table areas.
- Long-term, permanent retaining structures.
- Construction in urban environments where minimizing noise and vibration is crucial.
- Situations requiring high load-bearing capacity and structural stability.
Examples of Applications:
- Metro rail stations.
- High-rise building foundations.
- Dams and reservoirs.
- Tunnels and underground storage facilities.
When to Choose Sheet Piling?
- Temporary retaining walls for shallow excavations.
- Coastal protection and flood defenses.
- Projects requiring quick and cost-effective solutions.
- Situations where materials need to be reused.
Examples of Applications:
- Temporary excavation supports.
- Riverbank reinforcement.
- Flood control barriers.
- Quay walls and marine structures.
Key Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Diaphragm Walls:
- High Costs: Utilize advanced construction techniques and material optimization to reduce expenses.
- Specialized Equipment: Partner with experienced contractors equipped with the necessary machinery.
Sheet Piling:
- Limited Depth Capacity: Combine sheet piling with other solutions for deeper excavations.
- Noise and Vibration: Use modern, silent piling techniques to minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
Both Diaphragm Walls and sheet piling are essential retaining solutions, each with distinct advantages and applications. While Diaphragm Walls excel in providing long-term stability and water-tightness for deep excavations, sheet piling is an economical and versatile option for temporary or less demanding projects.
Selecting the right retaining structure depends on factors such as project depth, environmental conditions, budget, and timeline. Understanding these differences allows construction professionals to make informed decisions, ensuring the success and safety of their projects.
For high-load, permanent retaining solutions in challenging conditions, Diaphragm Walls are undoubtedly the superior choice. However, for quicker and more cost-effective temporary solutions, sheet piling remains a reliable alternative.