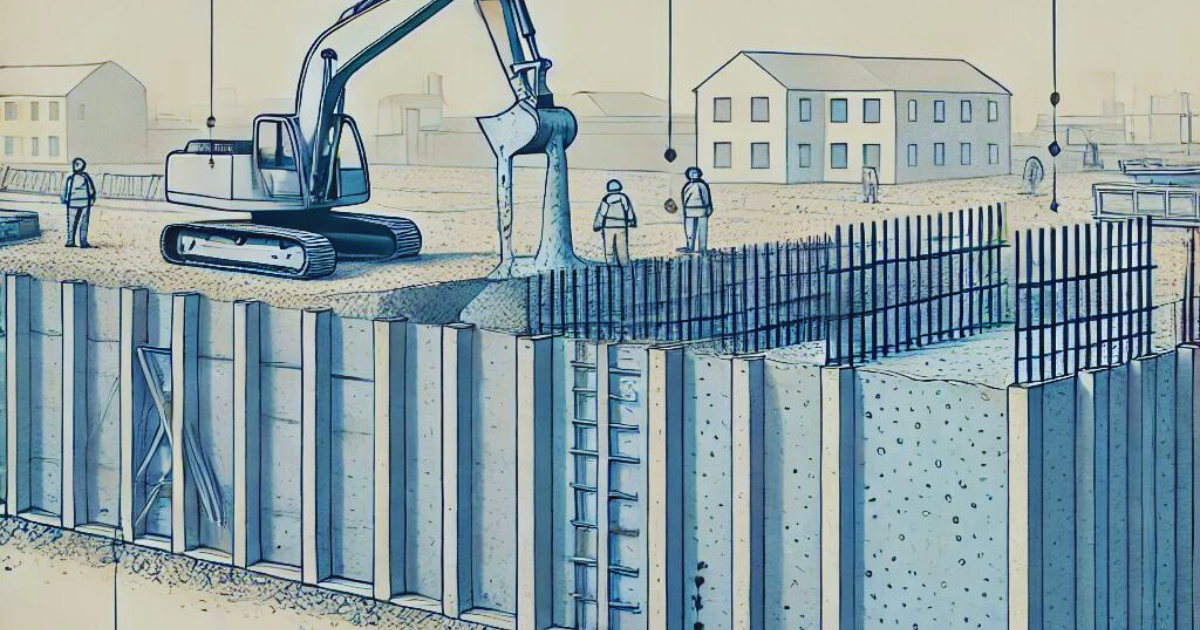
Slurry walls are a critical component of modern construction, playing an essential role in projects where controlling groundwater and stabilizing deep excavations is necessary. From high-rise building foundations to large-scale infrastructure projects, they provide a robust and reliable solution for soil retention and groundwater management. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the construction process, types, and numerous benefits in civil engineering projects.
What Are Slurry Walls?
Slurry walls are underground barriers built to prevent the flow of water or to provide structural support during excavation projects. Typically used in areas with high groundwater levels or unstable soils, they are constructed using a liquid mixture of bentonite clay and water, known as slurry. This slurry helps to maintain the stability of an open trench until permanent structural elements, such as concrete, are added to the wall.
They are commonly used in the construction of tunnels, dams, retaining walls, and deep foundations, particularly in urban settings where excavation is required adjacent to existing buildings or infrastructure. The method has gained widespread use due to its ability to handle deep excavations in challenging soil conditions.
How Slurry Walls Are Constructed
The construction involves several key steps that ensure both the stability of the trench and the long-term effectiveness of the wall. Here’s a breakdown of how slurry walls are built:
- Excavation of the Trench: The first step in constructing slurry walls is excavating a trench to the desired depth, which can range from a few meters to over 100 meters depending on the project. Excavation is typically performed using clamshells, grabs, or trench cutters, with the trench being dug in sections.
- Slurry Introduction: As the trench is excavated, a mixture of bentonite and water (or sometimes polymer-based materials) is continuously pumped into the trench. The slurry prevents the walls of the trench from collapsing by providing hydrostatic pressure, essentially supporting the trench as the soil is removed.
- Placement of Reinforcement: Once the trench is excavated to the required depth, steel reinforcement cages are lowered into the slurry-filled trench. These cages provide structural integrity to the wall once it’s completed and are a critical component in projects where the slurry wall needs to withstand significant loads.
- Concrete Pouring: After reinforcement is placed, concrete is poured into the trench, displacing the slurry upwards and out of the trench. The concrete typically flows from the bottom of the trench to the top, ensuring that it fully replaces the slurry and bonds with the reinforcement cages. The displaced slurry is collected, cleaned, and reused in the ongoing construction process.
- Curing and Finalization: Once the concrete has cured, the slurry wall is complete, providing a sturdy and waterproof barrier. Depending on the design, the wall may serve as a temporary or permanent structure in the project.
Types of Slurry Walls
It can be classified into different types based on the materials used and the method of construction. Understanding these types is essential for selecting the appropriate solution for a given project. Below are the primary types:
- Bentonite Slurry Walls: Bentonite slurry walls are the most common type and are typically used to control groundwater flow in soil or rock formations. Bentonite clay forms a gel-like consistency when mixed with water, which allows it to create a barrier that reduces water flow and stabilizes the trench during excavation.
- Cement-Bentonite Slurry Walls: In some cases, cement is added to the bentonite mixture to create a cement-bentonite slurry wall. This type offers both water containment and greater structural strength, making it ideal for projects where the wall will serve as a permanent structure.
- Polymer Slurry Walls: Polymer slurry walls use a synthetic polymer instead of bentonite, offering certain advantages in specific soil conditions. Polymer slurries tend to perform better in environments where bentonite might break down, providing greater stability over the long term.
- Soil-Cement-Bentonite (SCB) Walls: SCB slurry walls combine soil, cement, and bentonite in the slurry mixture. These walls are generally used in projects that require increased strength and are often employed in dam construction or large-scale environmental remediation projects.
Benefits of Slurry Walls
It offer numerous advantages in construction, particularly for projects that involve deep excavation, high groundwater levels, or unstable soils. Some of the key benefits include:
- Groundwater Control: One of the primary benefits of slurry walls is their ability to control groundwater flow. By forming a low-permeability barrier, slurry walls prevent water from seeping into the excavation site, allowing for safer and more efficient construction in wet or unstable conditions. This makes an essential tool in the construction of tunnels, dams, and other infrastructure projects located near bodies of water.
- Structural Support: Slurry walls provide critical structural support during deep excavations. The slurry mixture stabilizes the trench during the excavation process, preventing collapse and ensuring that adjacent buildings or infrastructure remain unaffected. In urban areas, slurry walls are particularly useful in protecting nearby structures during excavation for high-rise buildings or underground transit systems.
- Cost-Effective Solution: When compared to other methods of excavation and groundwater control, they are often more cost-effective, particularly in challenging soil conditions. The use of bentonite or polymer slurry reduces the need for additional structural elements, lowering material and labor costs. Additionally, slurry walls can be constructed relatively quickly, which helps keep projects on schedule and within budget.
- Environmental Benefits: Slurry walls are widely used in environmental remediation projects to contain contaminated soils and prevent the spread of hazardous materials. By forming an impermeable barrier, slurry walls help to prevent groundwater contamination and protect surrounding ecosystems. Additionally, slurry walls can be used to contain landfill sites, preventing leachate from entering the groundwater system.
- Versatility: Slurry walls are versatile and can be adapted to a wide range of projects, from large-scale infrastructure developments to smaller-scale civil engineering works. Whether controlling groundwater in a deep excavation or providing structural support in a dam, they are suitable for use in various environments and soil conditions.
- Long-Term Durability: Properly constructed slurry walls provide long-lasting durability, ensuring that they continue to function effectively for decades. With advancements in construction techniques and materials, modern slurry walls are capable of withstanding significant pressures and loads, making them a reliable choice for permanent structures.
Applications of Slurry Walls
They are used in a wide range of construction and civil engineering projects. Some common applications include:
- Foundations for High-Rise Buildings: Slurry walls are often used in urban areas to provide support during the excavation of deep foundations for skyscrapers. Their ability to control groundwater and prevent soil collapse is essential in maintaining the integrity of both the new structure and surrounding buildings.
- Tunnels and Subways: Slurry walls are a popular choice for constructing tunnels and subway systems, particularly in cities with high groundwater levels. They prevent water infiltration and provide structural support, allowing for safe excavation and tunnel construction.
- Dams and Water Retention Structures: In dam construction, slurry walls are used to create impermeable barriers that prevent water seepage through the foundation. This is critical in maintaining the stability of the dam and ensuring that it functions as intended.
- Environmental Remediation: Slurry walls play a vital role in environmental cleanup projects, where they are used to contain contaminated soil and groundwater. They prevent the spread of hazardous materials and help protect the environment from further contamination.
Conclusion
Slurry walls are an indispensable solution in modern construction, offering an effective and reliable method for controlling groundwater, stabilizing deep excavations, and providing long-term structural support. The versatility, combined with their environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness, makes them a valuable tool in a wide range of projects. By understanding how slurry walls are constructed and the benefits they provide, engineers and contractors can ensure the successful completion of complex construction tasks, particularly in challenging environments.